Accelerating Deep Learning Inference on Intel Arc 770: ONNX and PyTorch Go Head-to-Head
When deploying deep learning models, the choice of framework can significantly impact performance. PyTorch is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and dynamic computation graph, but when it comes to production, the need for speed and compatibility often leads developers to consider alternatives like Torch Script and ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange). In a recent benchmark, we put these frameworks to the test to see which one offers the best inference throughput for Resnet on both CPU and GPU. These tests gain additional significance as they were conducted on the 10th Gen Intel® Core™ i7(TM) 10610U processors and the Intel® Arc™ A770 GPU, showcasing how modern hardware can influence the efficiency of deep learning frameworks.
Disclaimer
Please note that the benchmarks presented here were conducted in a personal capacity and may not reflect official performance metrics. For authoritative and comprehensive benchmarking results, I encourage you to visit the official Intel website.
PyTorch: The Flexible Giant
PyTorch has become the go-to framework for many researchers and developers due to its ease of use and dynamic nature. It allows for rapid prototyping and debugging, making it an excellent tool for the development phase.
TorchScript: The Optimized Contender
TorchScript is PyTorch’s answer to the need for an optimized and deployable format. It enables the conversion of PyTorch models into a form that can run independently of Python, which is ideal for production environments where Python’s presence is not guaranteed or where performance is a critical factor.
ONNX: The Interoperable Speedster
ONNX stands out as an open standard for model representation, designed to facilitate model portability across different frameworks. It shines in environments where interoperability and hardware acceleration are required, making it a strong candidate for deployment.
Benchmarking Methodology
To ensure a fair and consistent comparison, we used a standard model architecture, ResNet-50, and measured the inference time across the three frameworks. The code snippet below outlines the process we followed, utilizing the Intel Extension for PyTorch (IPEX) to optimize the model execution on Intel hardware:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
import torch
import time
import onnxruntime
import torchvision.models as models
import intel_extension_for_pytorch as ipex
# Define your model architecture
model = models.resnet50()
model=model.to("xpu")
# Create a random input tensor
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
input_tensor = input_tensor.to("xpu")
# Pass the input tensor through the model
output_tensor = model(input_tensor)
# Convert the model to TorchScript
torchscript_model = torch.jit.trace(model, input_tensor)
# Convert the model to ONNX format
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
dummy_input=dummy_input.to("xpu")
onnx_filename = 'pytorchGraph.onnx'
torch.onnx.export(model, dummy_input, onnx_filename)
# Measure inference time for PyTorch
start_time = time.time()
output_tensor = model(input_tensor)
pytorch_inference_time = time.time() - start_time
print("PyTorch Inference Time:", pytorch_inference_time)
# Measure inference time for TorchScript
start_time = time.time()
output_tensor = torchscript_model(input_tensor)
torchscript_inference_time = time.time() - start_time
print("TorchScript Inference Time:", torchscript_inference_time)
# Measure inference time for ONNX
# Create an ONNX Runtime session
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnx_filename)
# Preprocess the input tensor
input_name = ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name
input_tensor =input_tensor.cpu().numpy()
start_time = time.time()
output_tensor = ort_session.run(None, {input_name: input_tensor})
onnx_inference_time = time.time() - start_time
print("ONNX Inference Time:", onnx_inference_time)
This code snippet demonstrates the conversion of a PyTorch model to both TorchScript and ONNX formats, followed by measuring the inference time for each framework. The use of the .to("xpu") method indicates that the model and tensors are being optimized for execution on Intel hardware using IPEX.
Benchmarking Inference Throughput: The Showdown
To objectively compare the inference throughput of PyTorch, TorchScript, and ONNX, we conducted a benchmark using a Resnet model. The model was run on both CPU and GPU to measure the time taken for inference. Here’s what we found:
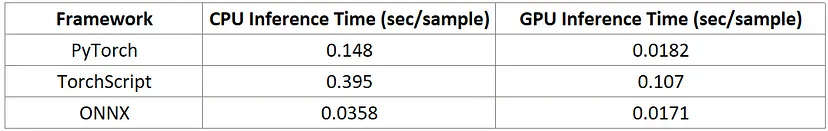
Comparative Inference Throughput of PyTorch, Torch Script, and ONNX on 10th Gen Intel® Core™ i7 and Intel® Arc™ A770 Hardware
CPU Inference: ONNX Takes the Lead
When it comes to CPU inference, ONNX stands out with the fastest time of 0.0358 seconds per sample, showcasing its ability to deliver high-speed performance in CPU-centric environments. PyTorch follows with a moderate time of 0.148 seconds per sample, while TorchScript trails at 0.395 seconds per sample. This significant difference highlights ONNX’s optimization for CPU inference, making it an attractive option for scenarios where GPU resources are limited or unavailable.
GPU Inference: A Tighter Competition
When it comes to GPU inference, the competition tightens with ONNX slightly outperforming PyTorch, delivering an inference time of 0.0171 seconds per sample compared to PyTorch’s 0.0182 seconds per sample. Despite the narrow margin, this showcases the efficiency of both frameworks in harnessing the capabilities of the Intel® Arc™ A770 GPU. TorchScript, with an inference time of 0.107 seconds per sample, appears to have untapped potential that could be realized with further optimization.
The near parity between ONNX and PyTorch in GPU inference suggests that both frameworks are robust choices for GPU-enabled environments.
Choosing the Right Framework for Deployment
The benchmark results provide a clear perspective on where each framework excels. ONNX emerges as the frontrunner in CPU inference and holds a competitive position in GPU performance. PyTorch, while not as fast as ONNX on the CPU, proves to be a strong contender on the GPU, making it a viable choice for GPU-accelerated applications. Torch Script’s performance indicates that it may require additional optimization to reach its full potential, particularly in CPU-bound scenarios.
In conclusion, the quest for the most efficient deep learning inference framework depends on a balance of speed, compatibility, and the unique demands of the production environment.